Which Way To Pitch Roof Based On Wind

It was fashionable for modern style homes built in the 1960s to have little pitch just a barely negligible slope to help drain water.
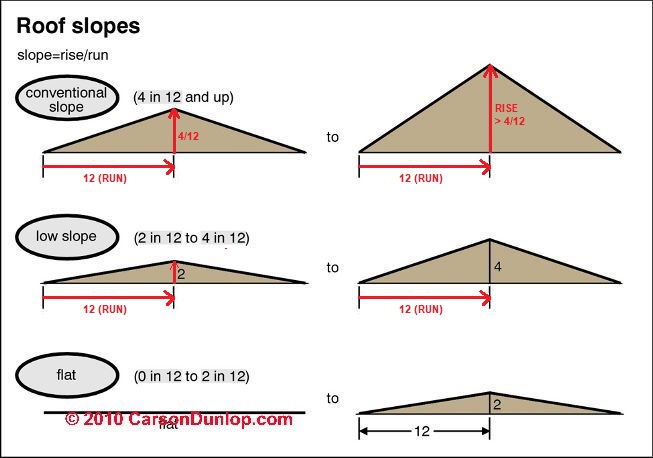
Which way to pitch roof based on wind. A single storm can destroy a roof in many cases. Lower slopes don t handle wind driven rain as well. A typical 2 slope gable roof is often times cheaper to build but it allows the wind to catch the roof and it is much more easily blown away. A flat roof would have a 2 12 pitch while the average roof pitch would be between 4 12 and 9 12.
A 30 degree roof slope 7 12 pitch is the right pitch to aerodynamically handle high wind. A roof at 9 12 is considered a very high pitch. But there are things you can do to protect your roof and therefore your home. The minimum roof pitch for shedding snow is around 30 or a 6 12 or 7 12 slope although this is not a definite as the material of your roof the direction of the snow and wind are some factors that can affect whether or not snow will slide as roofs of as little as 10 have been reported to shed snow.
A roofing system isn t just 5 smart tips for choosing the best roof for high winds read more. Because mid range slope roofs withstand strong winds better than steep roofs keep the roof pitch below 6 12 and greater than 4 12. Pitch is a measure of the steepness of a roof. The hip style roof can stand up to high winds when a storm comes.
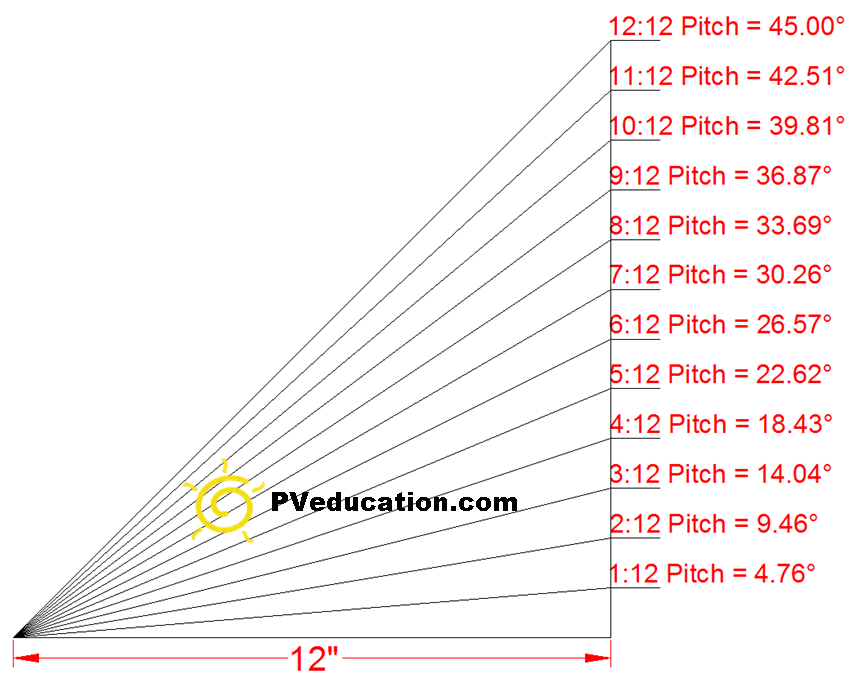
Pitch is usually described as a ratio of vertical rise in inches for every 12 inches of horizontal surface. Building a 4 slope hip style roof has been found to lessen the load of the wind on the house. Build a moderately pitched hip roof. Roof pitch refers to the angle of your roof or how steeply it slopes.
High wind regions key issues n special installation methods are recommended for asphalt roof shingles used in high wind coastal regions i e greater than 90 mph gust design wind speed. A 2 12 roof which rises two inches for every 12 inches covered is considered a very low pitch. Any pitch higher than 9 12 is considered a steep pitch. Roofs on victorian era houses were often sharply angled with a steep pitch.
N use wind resistance ratings to choose among shingles but do not rely on ratings for performance. Flat roofs increase uplift forces on the overhang and are more prone to leaks. And ironically one of the biggest factors in damage to a roof is windblown debris often the debris of other people s failed roofs. Steeper slopes increase the sail effect that makes them susceptible to wind.
Visually this roof appears flat.