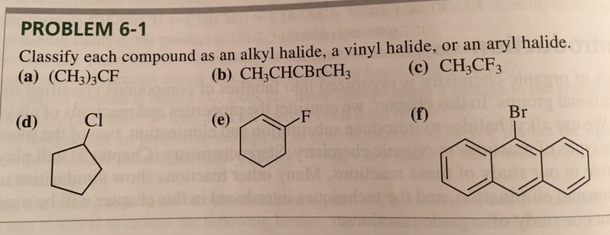What Is A Vinyl Alkyl Halide
In aryl halides the halogen bearing carbon is part of.
What is a vinyl alkyl halide. Vinyl or more specifically pvc is also used in plastic pipes synthetic leather records hence the name vinyl record insulation and many other products. Halogens are more electronegative than carbon. Other articles where vinylic halide is discussed. Structure and physical properties.
Start with an alkyl halide and. However alkyl halides may sometimes be confused with aryl halides. The functional group of alkyl halides is a carbon halogen bond the common halogens being fluorine chlorine bromine and iodine. For example if the halogen atom is attached to a carbon atom which is attached to a benzene ring cl ch 2 c 6 h 5 one would think it is an aryl halide but it is an alkyl halide because the halogen atom is attached to the carbon that is sp 3 hybridized.
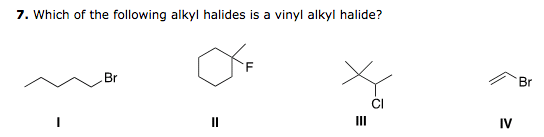
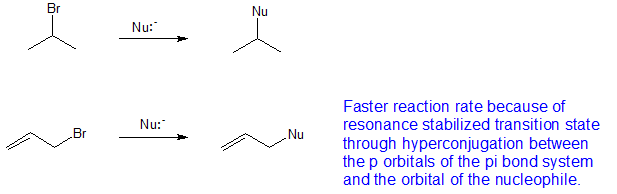
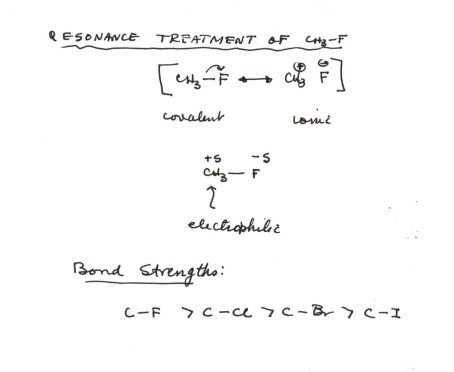
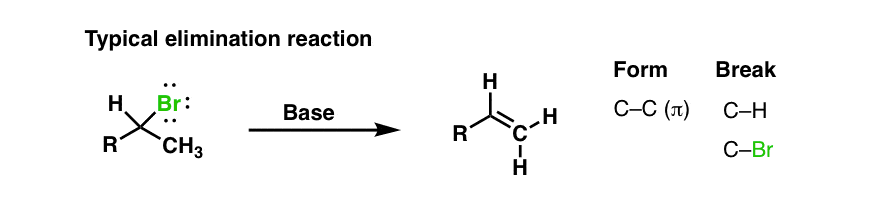
In vinylic halides the carbon that bears the halogen is doubly bonded to another carbon. Alkyl halides fall into different classes depending on how the ha. A vinyl halide is clearly a species with a formula h 2c c x h in which a halide is directly bound to an olefinic bond formally this is ethylene h 2c ch 2 with one of the hydrogens substituted by a heteroatom vinyl chloride h 2c chcl is an example. With the exception of iodine these halogens have electronegativities significantly greater than carbon.
The extra strength of the carbon halogen bond in aryl halides. The carbon chlorine bond in chlorobenzene is stronger than you might expect. Finally halo is prefixed to it. Other articles where tertiary alkyl halide is discussed.
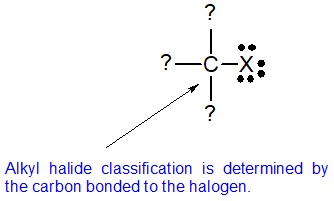
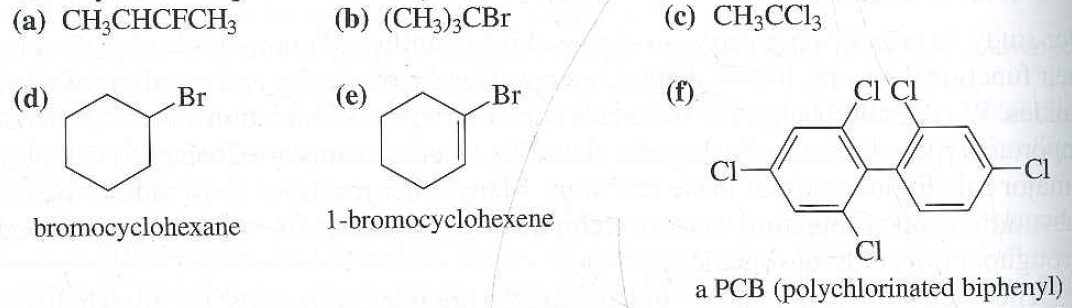
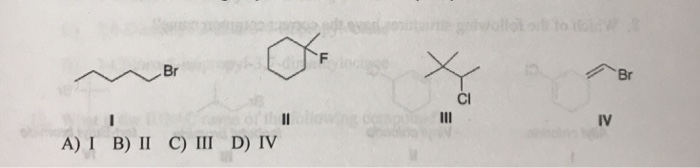
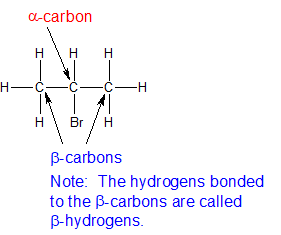
In alkyl halides all four bonds to the carbon that bears the halogen are single bonds. Iupac nomenclature of alkyl halide or haloalkanes in substitutive system of iupac nomenclature the alkyl halides are named as haloalkanes. In a primary alkyl halide the carbon that bears the halogen is directly bonded to one other carbon in a secondary alkyl halide to two and in a. Classified as primary secondary or tertiary according to the degree of substitution at the carbon to which the halogen is attached.
Halogens are treated the same way as alkyl groups. In this system a root word is chosen based on the number of carbon atoms present in the parent chain and then the primary suffix ane is added. Consequently this functional group is polarized so that the carbon is electrophilic and the halogen is. The name of the halogen is followed by the name of the.
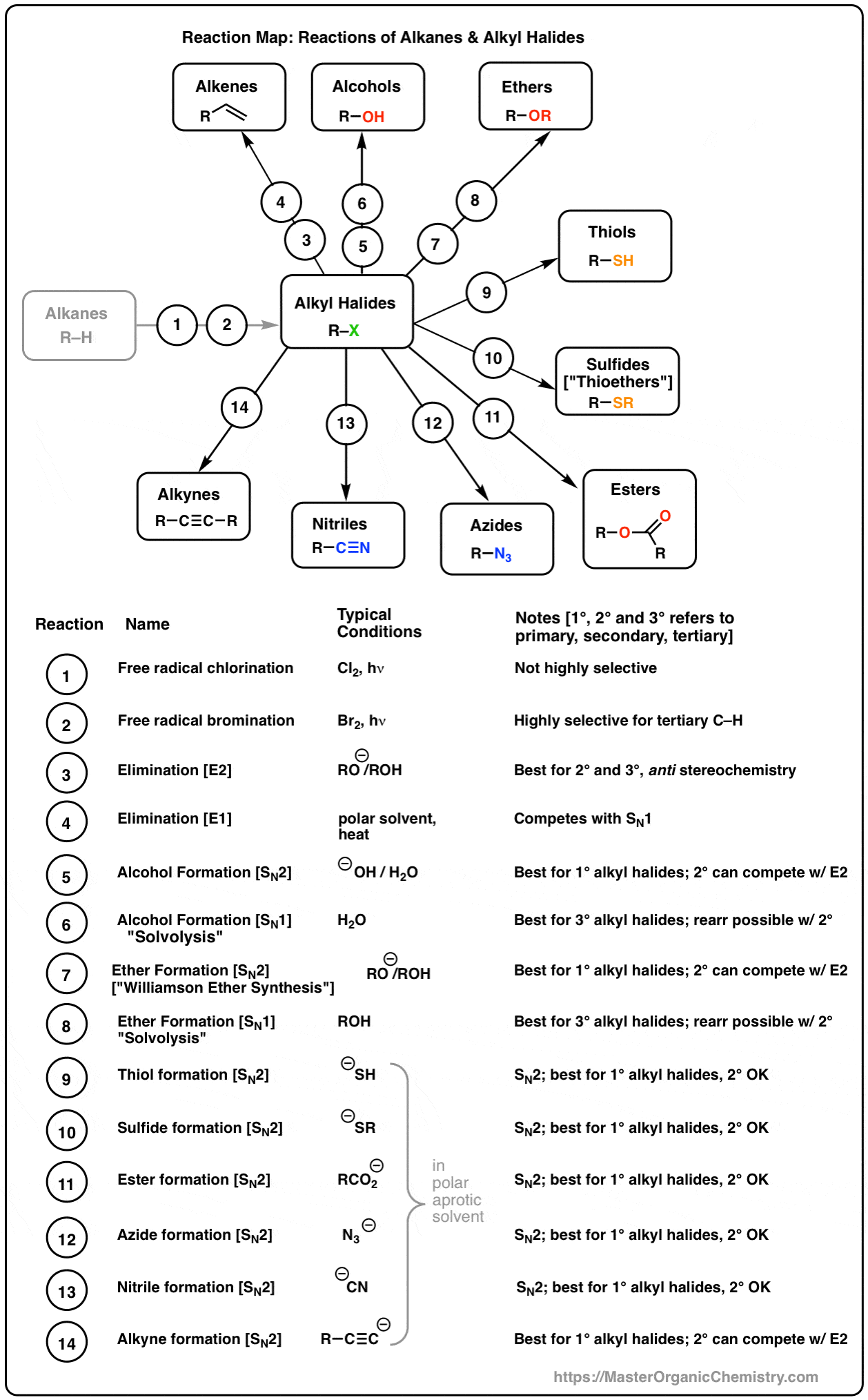
Alkyl halides also known as haloalkanes are compounds in which one or more hydrogen atoms in an alkane have been replaced by halogen atoms fluorine chlorine bromine or iodine. The iupac nomenclature shown in brackets in the illustration below considers an alkyl halide a substituted alkane i e. They are subdivided into alkyl vinylic aryl and acyl halides. An aryl halide has general formula c 6h 5x in which an halide group x has substituted the aryl ring.