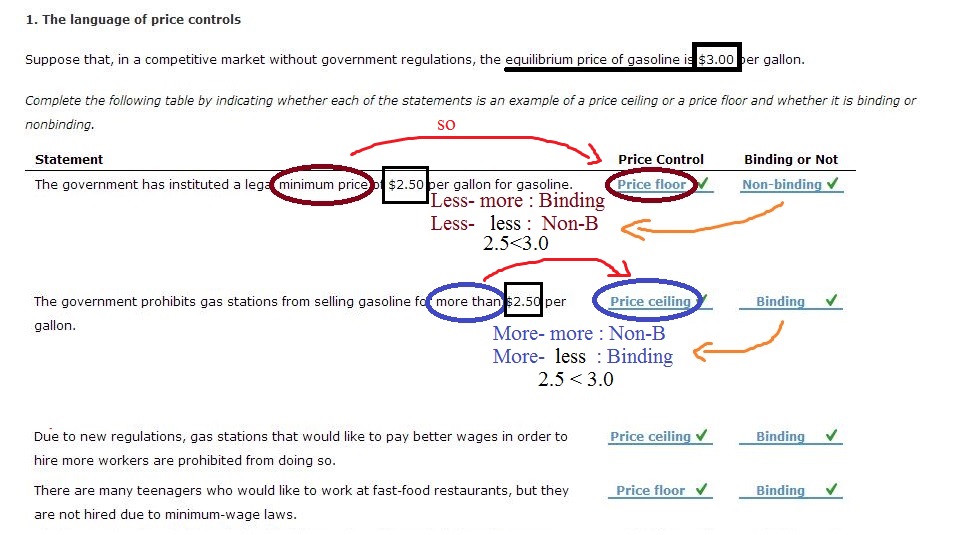
What Is A Price Floor And What Are Its Economic Effects

Government enforce price floor to oblige consumer to pay certain minimum amount to the producers.
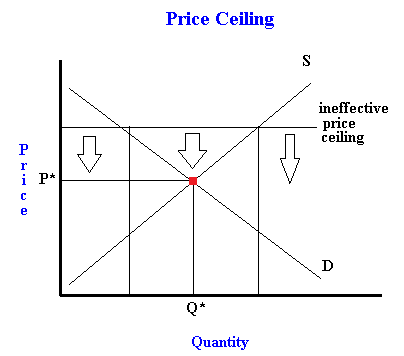
What is a price floor and what are its economic effects. By observation it has been found that lower price floors are ineffective. However price floor has some adverse effects on the market. The most common price floor is the minimum wage the minimum price that can be payed for labor. Price floor is enforced with an only intention of assisting producers.
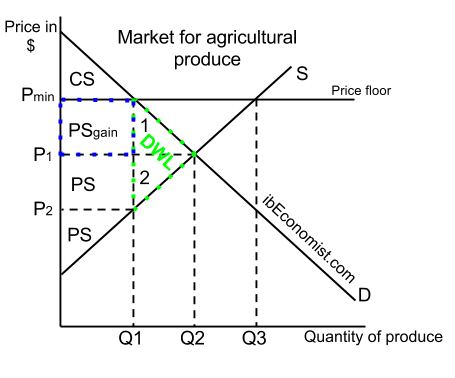
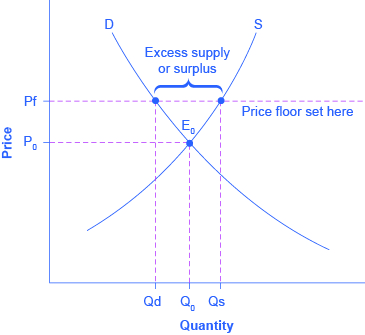
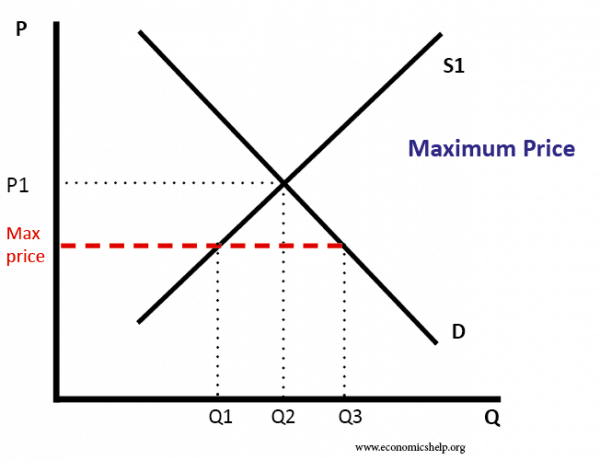
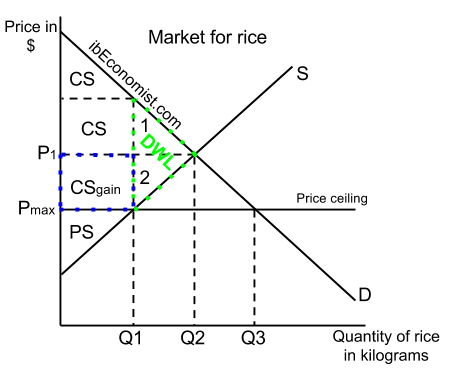
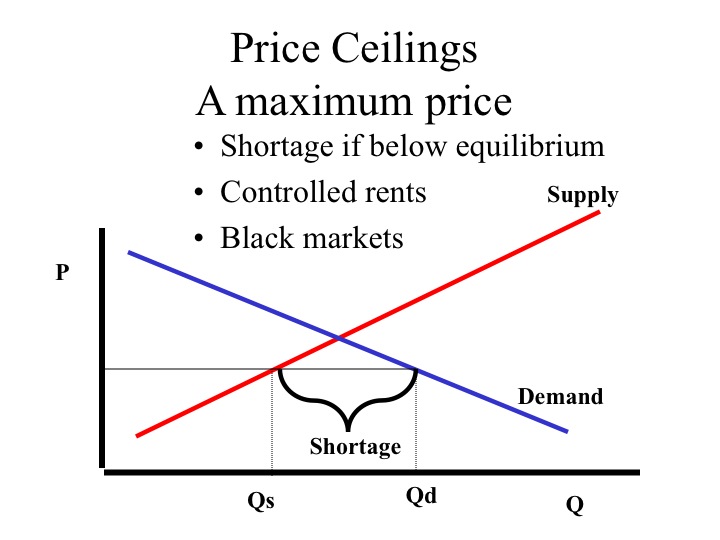
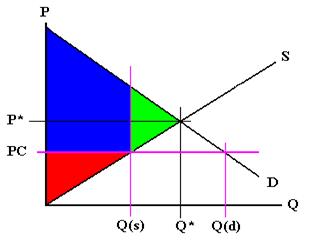
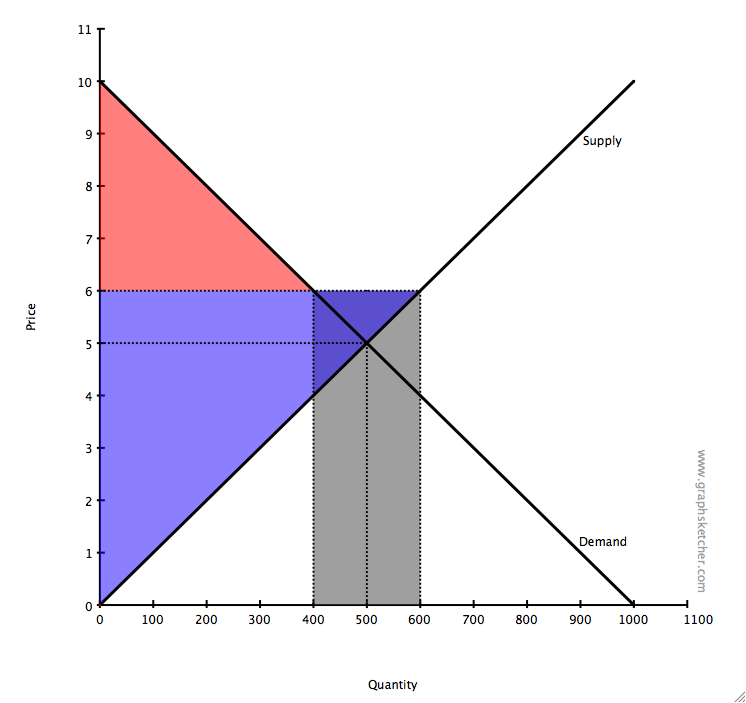
The equilibrium price commonly called the market price is the price where economic forces such as supply and demand are balanced and in the absence of external. Governments usually set up a price floor in order to ensure that the market price of a commodity does not fall below a level that would threaten the financial existence of producers of the commodity. A price floor is the lowest legal price a commodity can be sold at. Price floor is a situation when the price charged is more than or less than the equilibrium price determined by market forces of demand and supply.
A price floor must be higher than the equilibrium price in order to be effective. Price floors are used by the government to prevent prices from being too low. Price floors are also used often in agriculture to try to protect farmers. A price floor is an established lower boundary on the price of a commodity in the market.
Price floor has been found to be of great importance in the labour wage market. Types of price floors 1. In this case since the new price is higher the producers benefit. A price floor is a government or group imposed price control or limit on how low a price can be charged for a product good commodity or service.























/QuantitySupplied2-98c4fd9fe04e4ec78318d9dd87f2c93e.png)


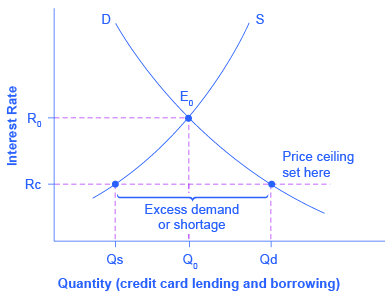
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/WhyYouCantInfluenceGasPrices3-257334e47bc54cd7a449da9df90814af.png)