What Is A Ceramic Capacitor Made Of

Characteristics precision and tolerances.
What is a ceramic capacitor made of. Class 1 and class 2. The electrodes are now printed onto the ceramic sheets using a screen printing process. The electrode ink is made from a metal powder that is mixed with solvents and ceramic material to make the electrode ink. Ceramic disc capacitors have a capacitance value of about10pf to 100μf with a wide variety of voltage ratings between 16v to 15 kv and more.
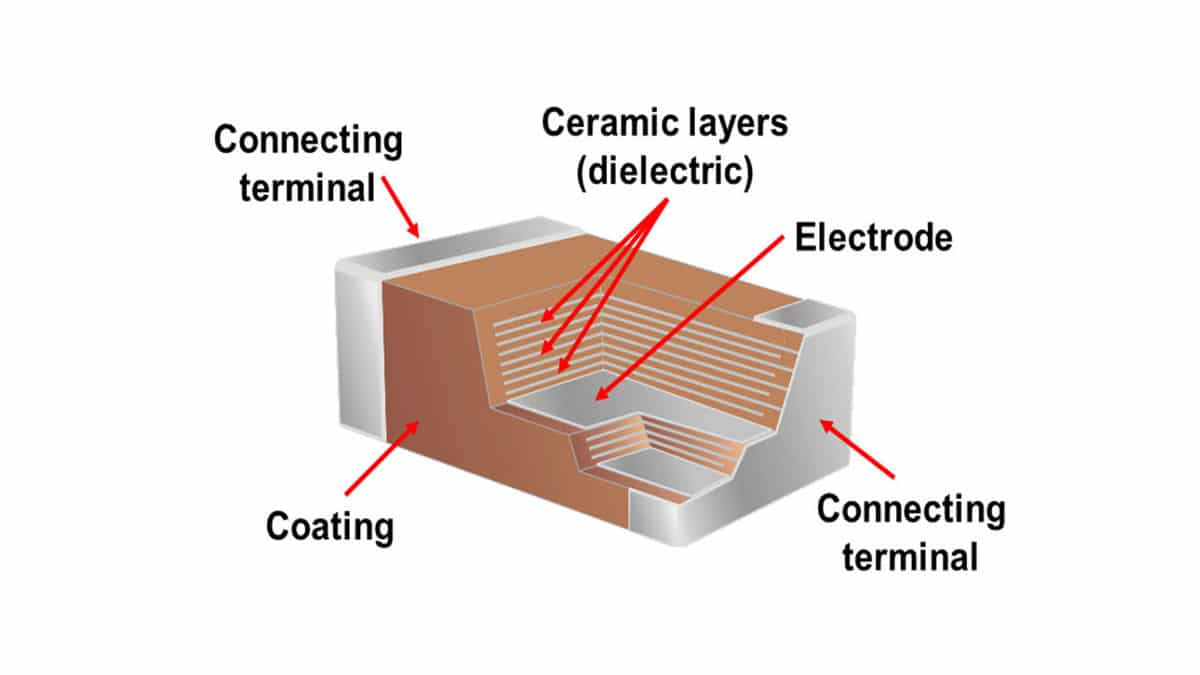
The capacitors in which the ceramic material such a paralectric titanium oxide or ferroelectic is used as the insulating material or dielectric is known as the ceramic capacitors. There are two classes of ceramic capacitors available today. Ceramic capacitor definition a ceramic capacitor is a capacitor which uses a ceramic material as the dielectric. Ceramic capacitors are classified as type i type ii or type iii.
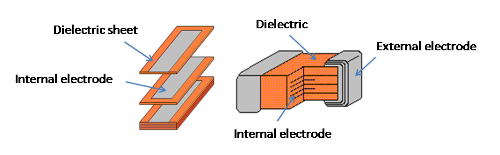
The type i ceramic capacitor generally has a dielectric made from a mixture of metal oxides and titanates. A ceramic capacitor is a fixed value capacitor where the ceramic material acts as the dielectric it is constructed of two or more alternating layers of ceramic and a metal layer acting as the electrodes the composition of the ceramic material defines the electrical behavior and therefore applications. Ceramic disc capacitors are made by coating a ceramic disc with silver contacts on both sides as shown above illustrates. A capacitor consists of two conductors separated by a non conductive region.
These are used in resonant circuits filters and. Screen printing and stacking. The non conductive region can either be a vacuum or an electrical insulator material known as a dielectric examples of dielectric media are glass air paper plastic ceramic and even a semiconductor depletion region chemically identical to the conductors. The ceramic capacitor is made by making a finely grounded powder of a dielectric material which is either paraelectric material like the titanium.
They have high insulation resistance and lower frequency losses and maintain a stable capacity even when voltage varies. The thickness of the sheet determines the voltage rating of the capacitor.