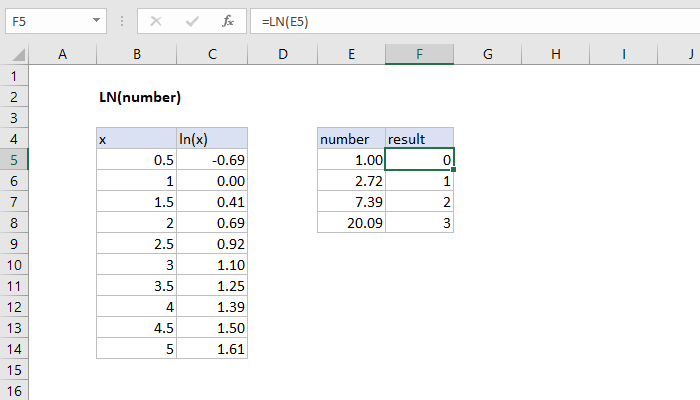
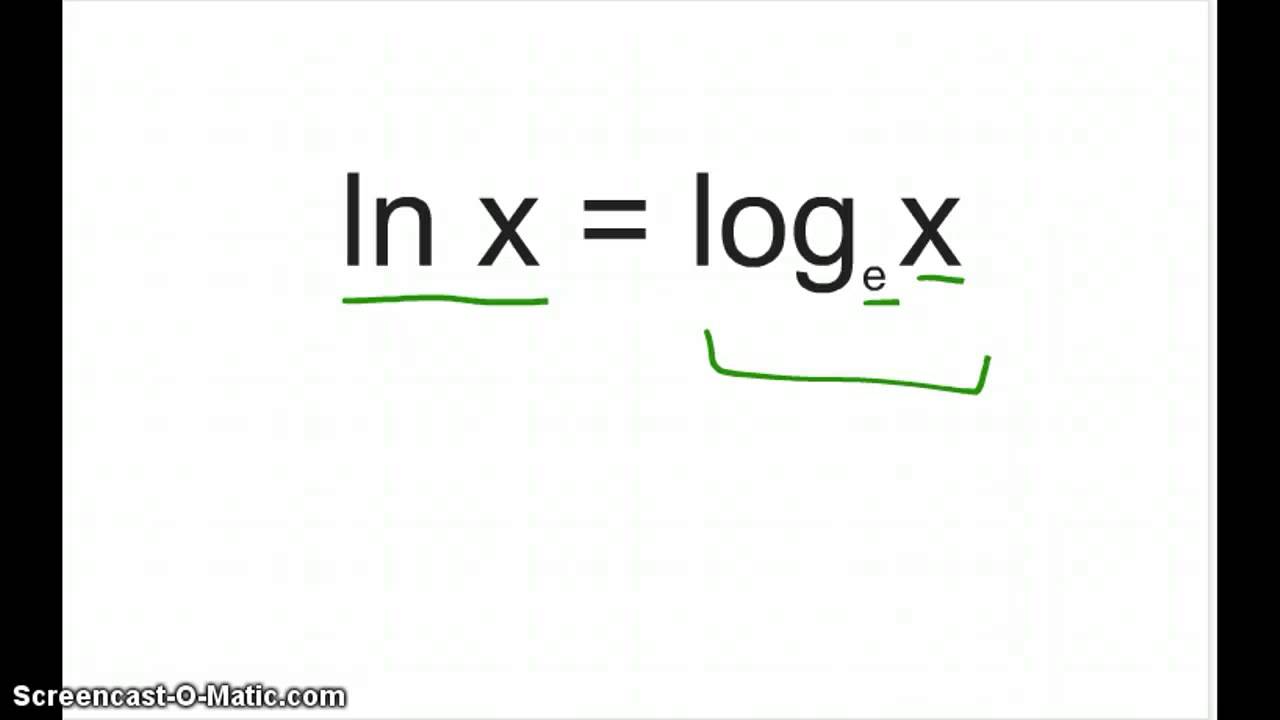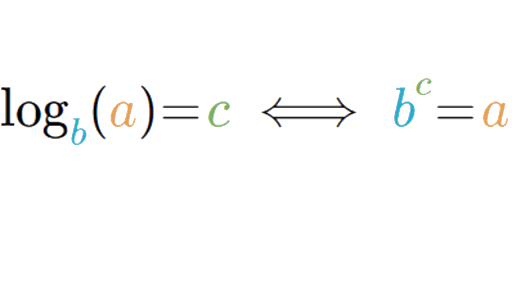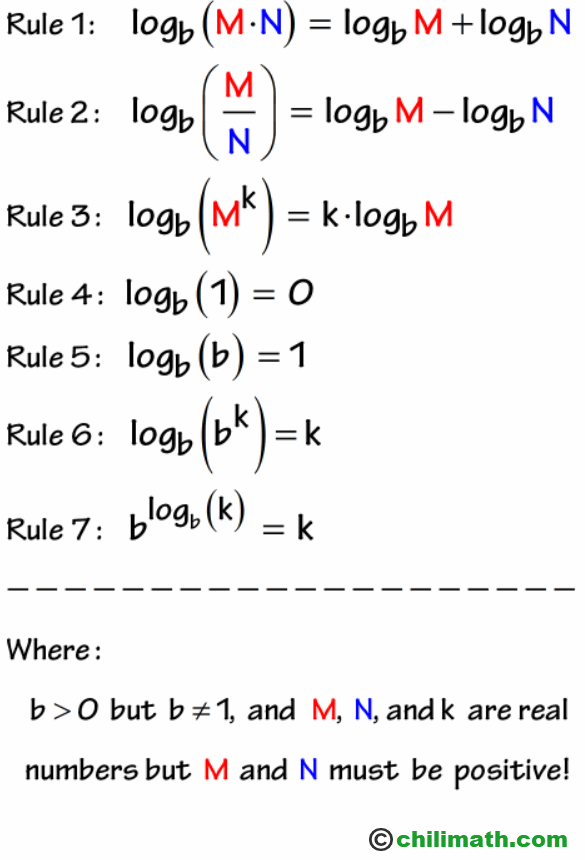What Does Ln Do In Math

Parentheses are sometimes added for clarity giving ln x log e x or log x.
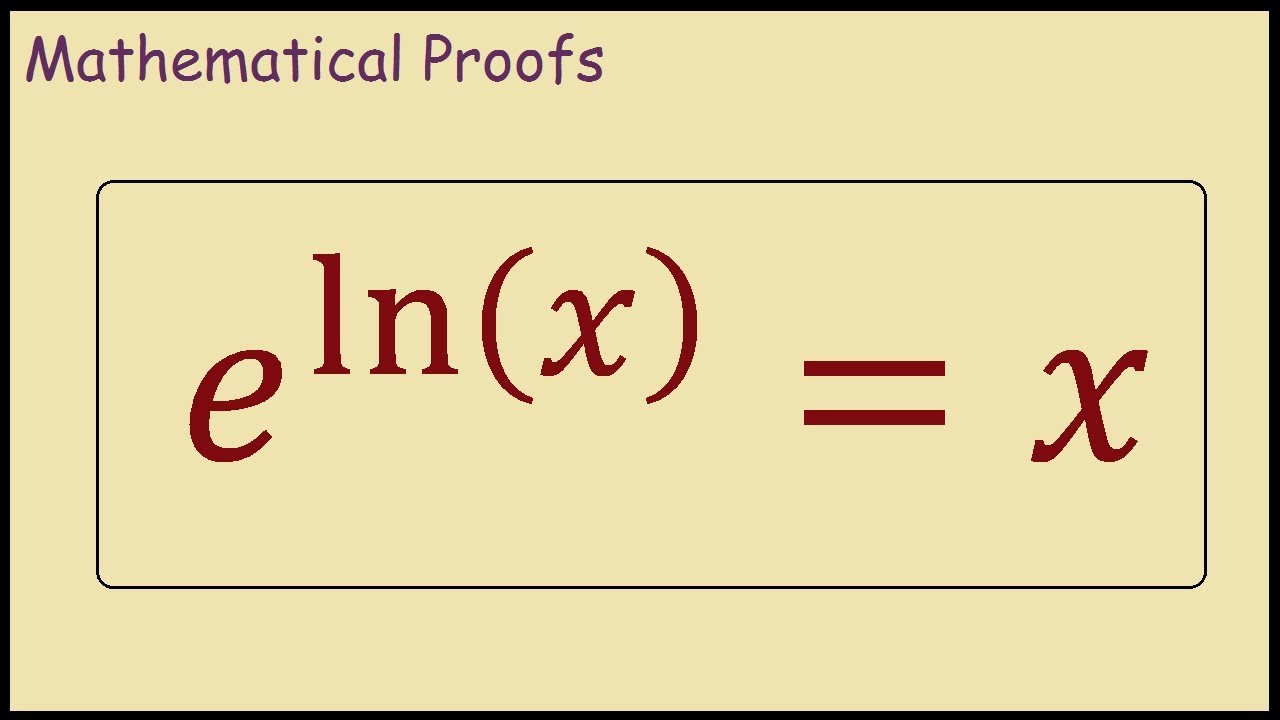
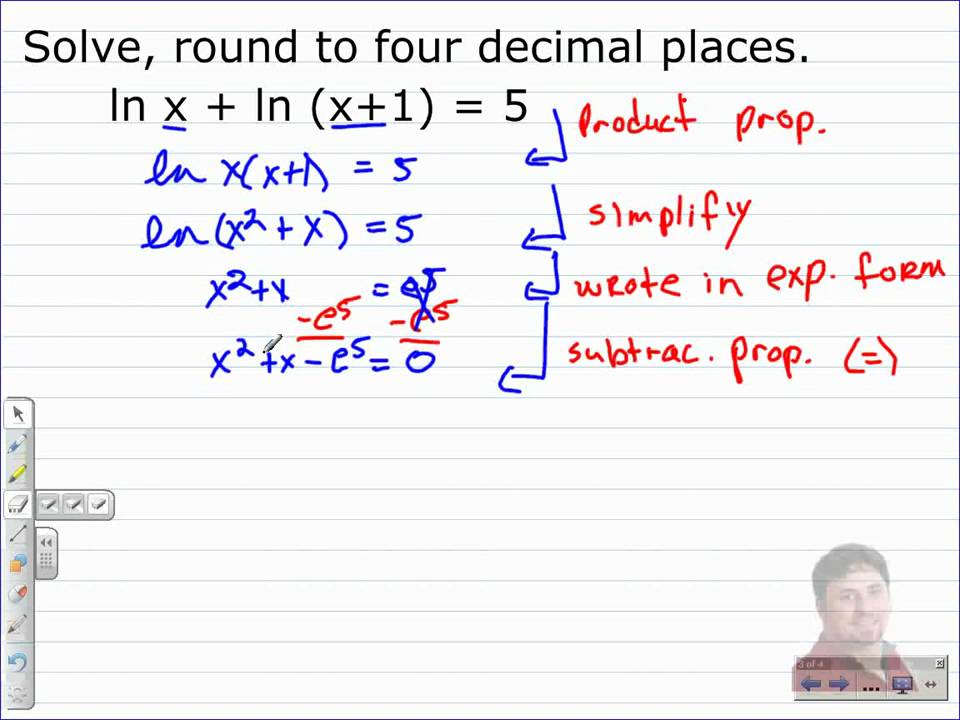
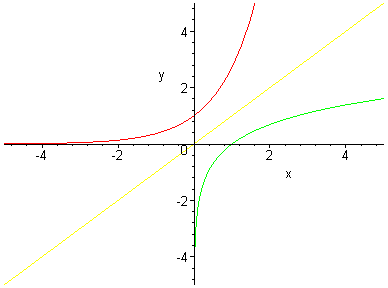
What does ln do in math. The limit of natural logarithm of infinity when x approaches infinity is equal to infinity. Natural logarithm of infinity. So the natural logarithm of e is equal to one. Ln e log e e ln e is the number we should raise e to get e.
Ln 5 2 2 ln 5 key natural log properties. The natural logarithm of zero is undefined. Log 100 this usually means that the base is really 10. But e is the amount of growth after 1 unit of time so ln e 1.
The limit near 0 of the natural logarithm of x when x approaches zero is minus infinity. Ln e log e e 1. Ln e is the amount of time it takes to get e units of growth about 2 718. Ln x log e x so the natural logarithm of e is the base e logarithm of e.
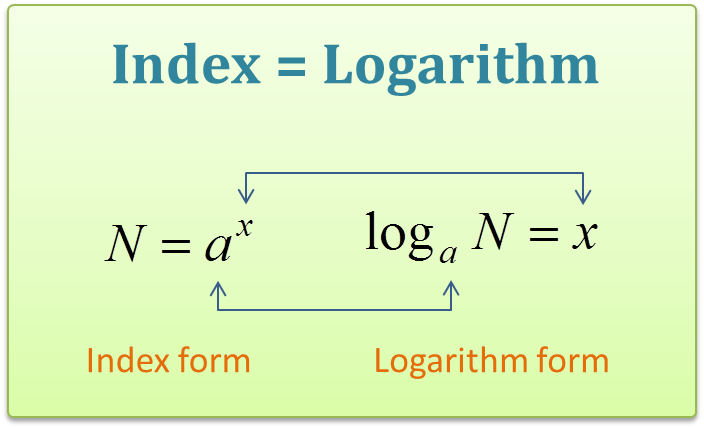
In mathematical terms a logarithm of a number is the exponent that is used to raise another number the base in order to arrive at that number. It is called natural because it uses the mathematical constant e 2 718. Ln x y y ln x the natural log of x raised to the power of y is y times the ln of x. On a calculator it is the log button.
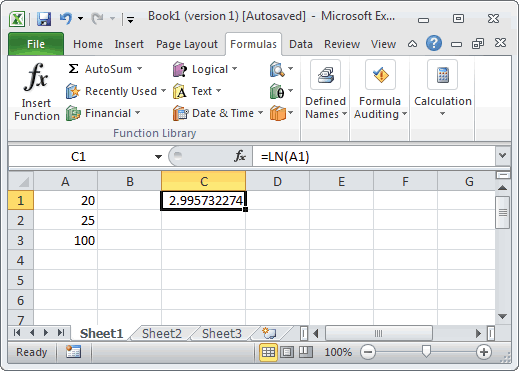
Sometimes a logarithm is written without a base like this. The math robot says. E 1 e. The natural logarithm of a number x is defined as the base e logarithm of x.
A logarithm ln is a concept in mathematics that denotes the number of times a number has to be multiplied by itself in order to arrive at a specified value. Because they are defined to be inverse functions clearly ln e 1 the intuitive human. Engineers love to use it. The natural logarithm of a number is its logarithm to the base of the mathematical constant e where e is an irrational and transcendental number approximately equal to 2 718 281 828 459 the natural logarithm of x is generally written as ln x log e x or sometimes if the base e is implicit simply log x.
You also sometimes see the function log x which uses 10 in its definition instead of e. It is called a common logarithm.