What Causes Thickening Of The Bladder Wall In Dogs

Common causes of bladder wall thickening include.
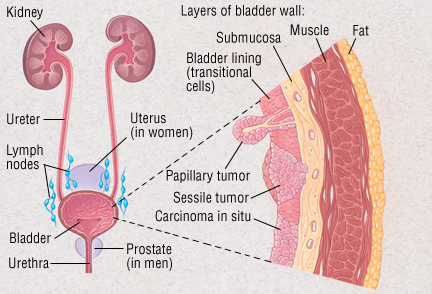
What causes thickening of the bladder wall in dogs. The actual canine thickened bladder wall cannot be seen by the owner of course so other signs and symptoms must be used to alert owners of a problem. There are various types of bladder tumors like squamous cell carcinoma arise in the epithelial cells adenocarcinoma arise in the glandular epithelium. Older dogs are more prone to this condition however. Here are the symptoms causes and conventional treatment of canine bladder cancer.
Bladder cancer in dogs usually occurs in the form of canine transitional cell carcinoma tcc. Some of these factors include polyps fungal infections tumors bacterial infections and bladder or urinary stones. This condition is caused by microbes usually bacteria which enter into the bladder of a dog and proliferate. The most common cause of canine thickened bladder wall in dogs of all ages is an infection caused by bacteria.
Bacterial infections usually cause hematuria and dysuria straining to urinate. Other common causes include stones polyps tumors and fungal infections. The thickening of the bladder wall can be caused by a number of factors. In fact it is estimated that 14 of dogs will get a bladder infection in their lifetime.
The first group of tests performed includes urinalysis urine culture and bladder palpation. The most common cause of cystitis in dogs is an infection caused by bacteria. Description urinary bladder cancer accounts for approximately 2 of all reported malignancies in dogs with more than 60 million dogs in the usa deaths from urinary bladder cancer are increasing rapidly. Other common causes include bladder stones tumors or polyps in the bladder and abnormal anatomy.
Bladder cancer surgery. Inflammation due to urinary tract infection uti a uti is often the result of bacteria entering the urethra and then the bladder. By definition cystitis means inflammation of the bladder. This type of canine cancer is fairly aggressive and can spread to other parts of the body.
A thickened bladder wall often occurs in dogs no matter what age.