What Causes Lamination In A Rock

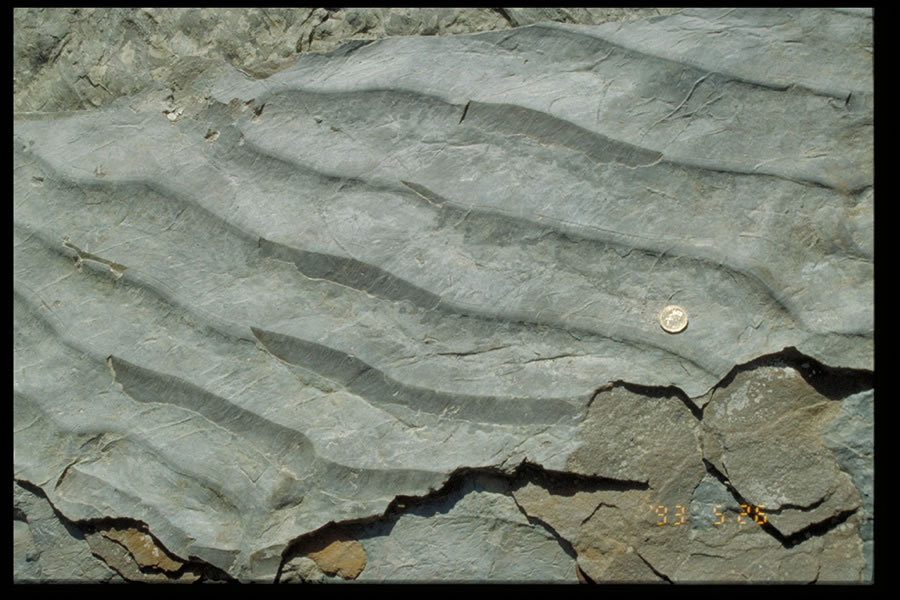
Lamina that occurs in sedimentary rocks laminae are normally smaller and less pronounced than bedding lamination is often regarded as planar structures one centimetre or less in thickness whereas bedding layers are greater than one centimetre.
What causes lamination in a rock. The laminate is joined with the substrate carrying solar cells as the foils are pressed together between two heated rolls. Lamination has become a regular part of the converting process. However structures from several millimetres to many centimetres. But the age old problems of layflat and air bubbles will always cause worry unless you and your supplier use three basic measurements.
Thus lamination consists of thin units in bedded or layered sequence in a natural rock succession whereas stratification consists of bedded layers or strata in a geologic sequence of interleaved sedimentary rocks. Besides being easier to handle this lamination process also allows use of thinner. Figure 7 21 shows the hot lamination of opv modules. Plate lamination defect acceptance criteria.
In geology lamination is a small scale sequence of fine layers laminae. External stratification more beds and the term lamina is sometimes applied to a unit less than one centimetre in thickness. This causes the adhesive to melt momentarily and upon cooling it forms a tight seal. Edge lamination defect can reduce the integrity of connections made to the edge of a plate.
The results show that regular lamination can cause size effect even without considering size effect of the intact rock and rock joints. It s hard to find a paper film or foil product that isn t a laminate.