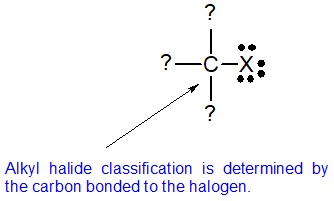
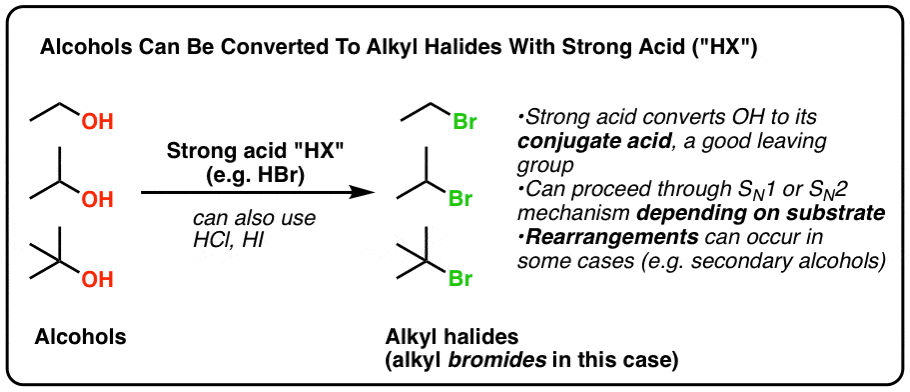
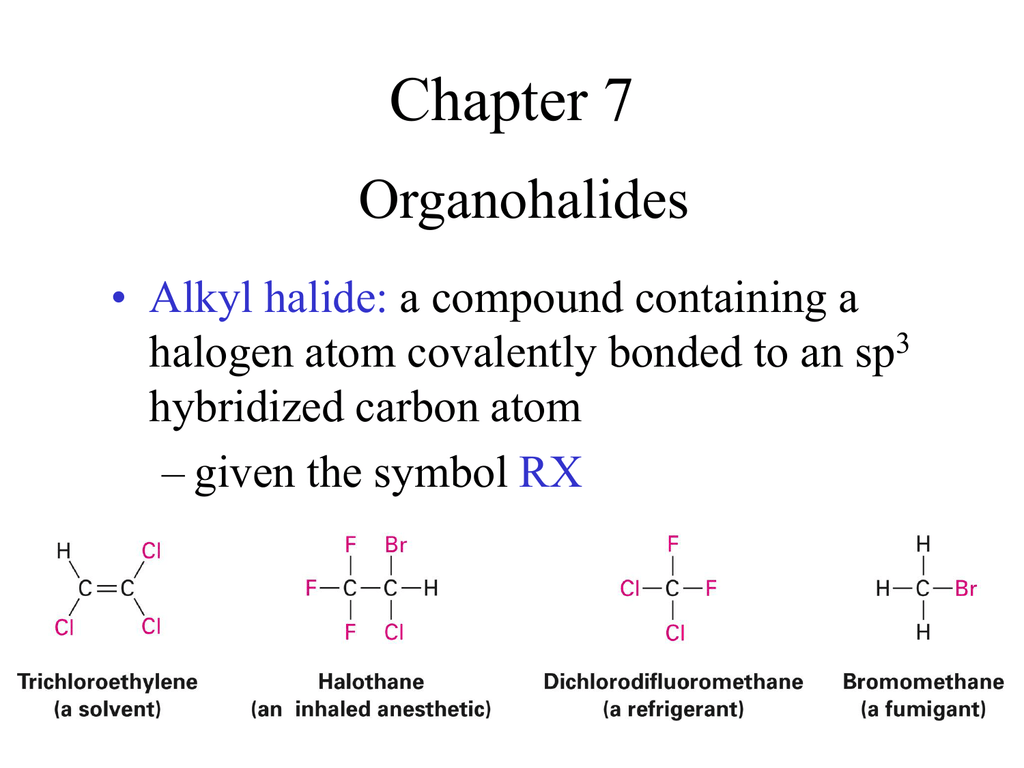
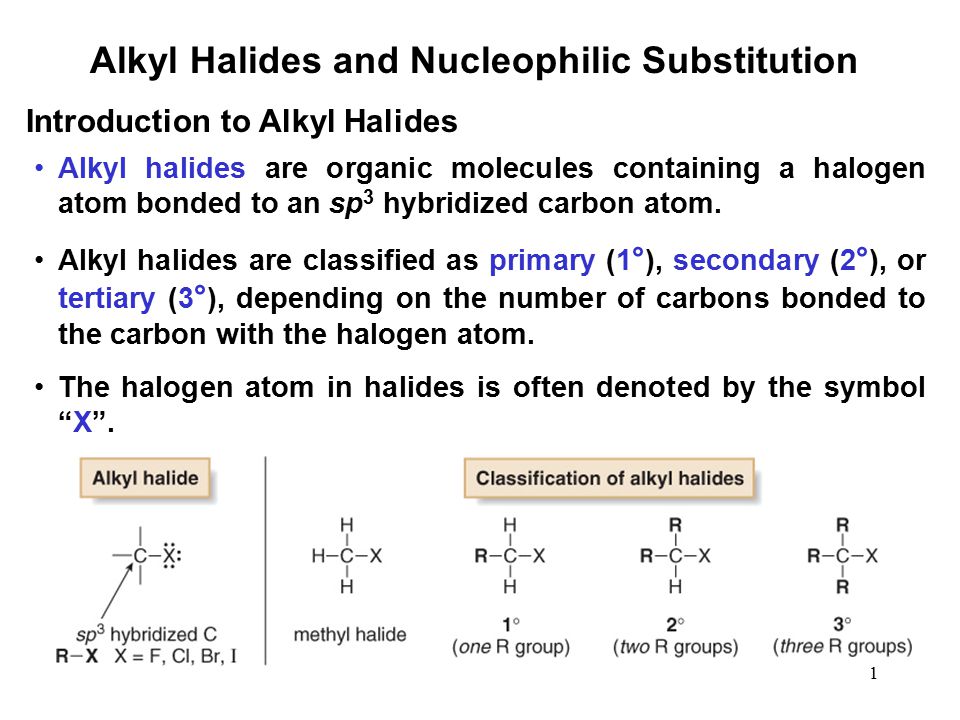
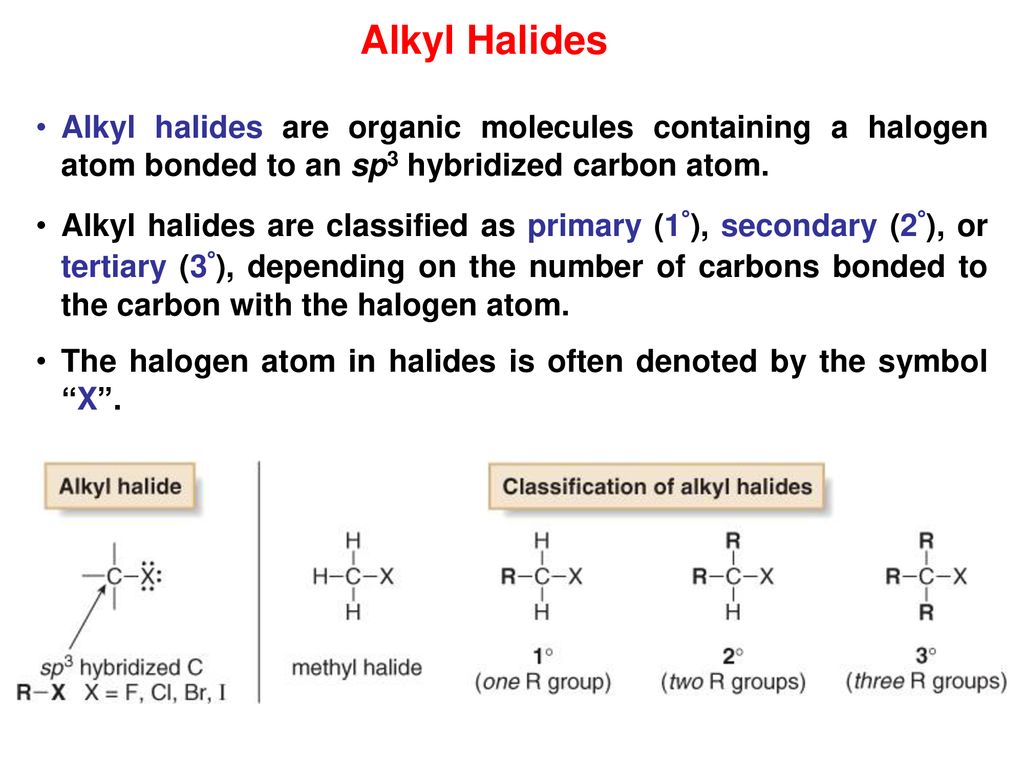
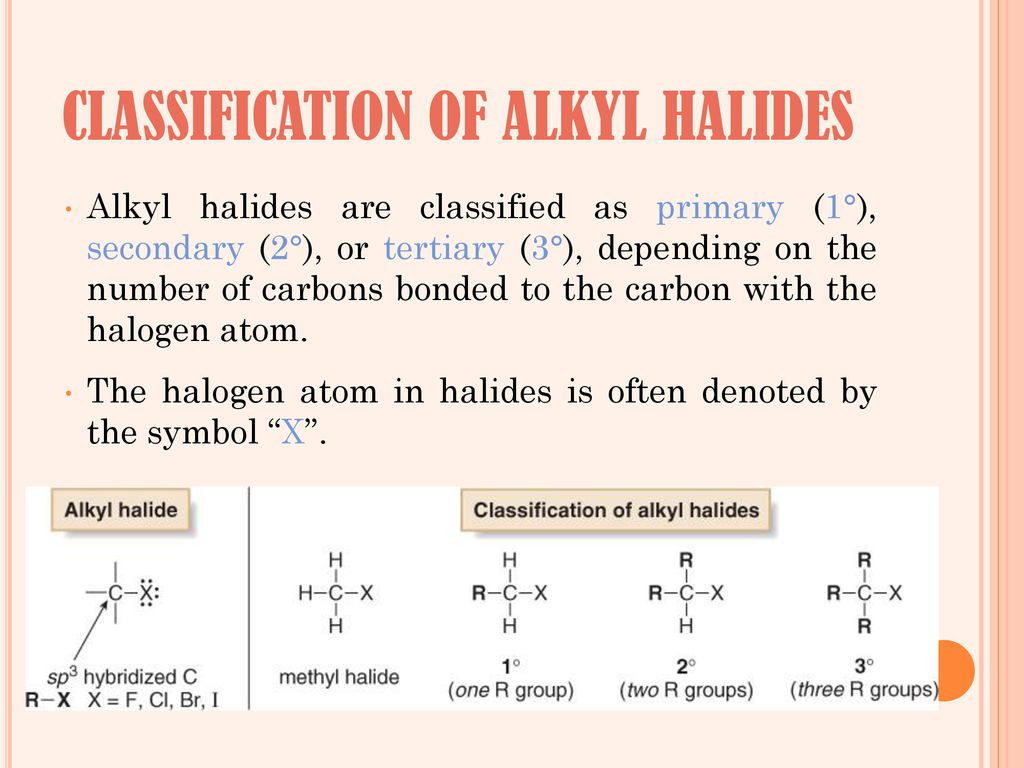
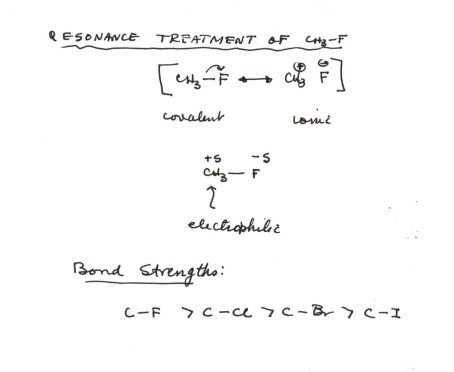
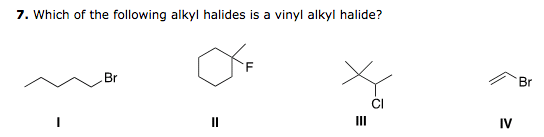
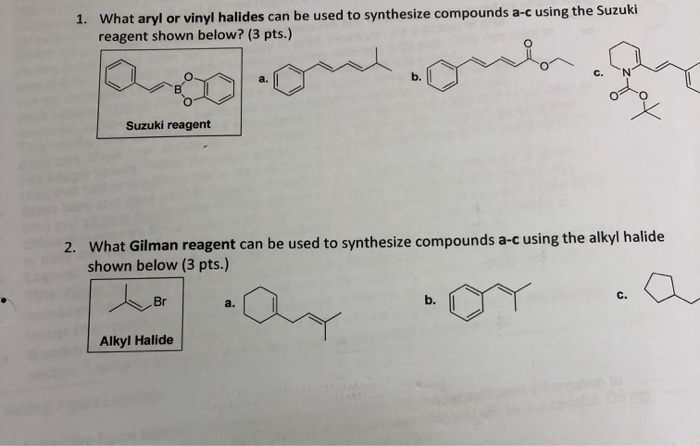
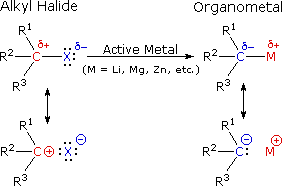What Are Vinylic Halides And Alkyl

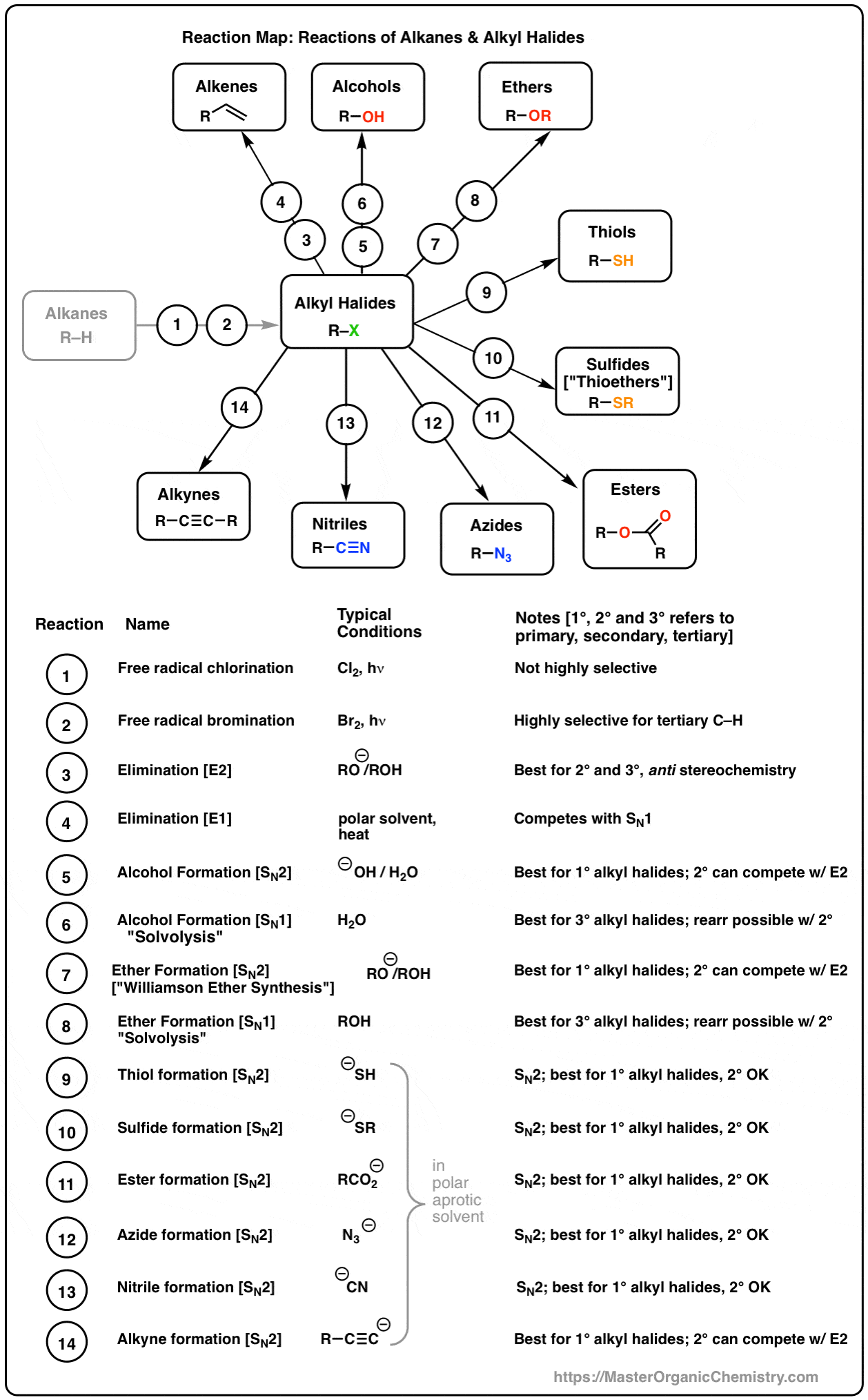
The following table summarizes the expected outcome of alkyl halide reactions with nucleophiles.
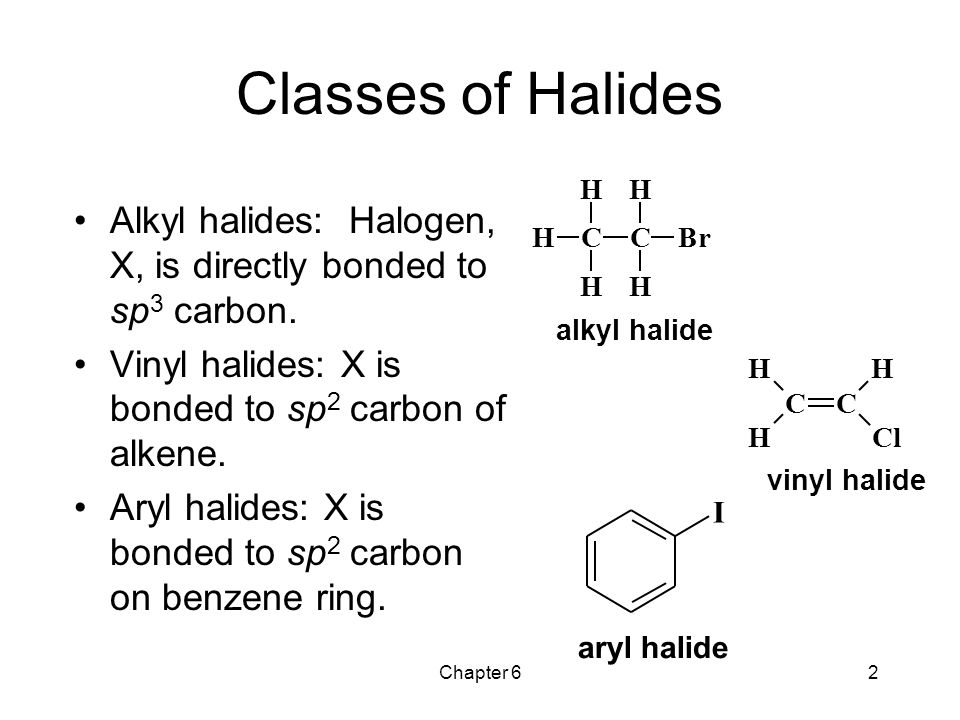
What are vinylic halides and alkyl. An aryl halide has general formula c 6h 5x in which an halide group x has substituted the aryl ring. In organic chemistry a vinyl halide is a compound with the formula ch 2 chx x halide the term vinyl is often used to describe any alkenyl group. A vinyl halide is clearly a species with a formula h 2c c x h in which a halide is directly bound to an olefinic bond. Acetone ethanol tetrahydrofuran ethyl acetate are used.
Vinylic halides resemble alkenes in that they undergo addition to their double bond. It is assumed that the alkyl halides have one or more beta hydrogens making elimination possible. For this reason alkenyl halides with the formula rch chx are sometimes called vinyl halides. Firstly if the nuclophile comes in on the s n 2 path it will bump into a hydrogen or other group which is trans to the leaving group.
Vinyl chloride h 2c chcl is an example. They are subdivided into alkyl vinylic aryl and acyl halides. Vinylic halides may be converted to grignard reagents by reaction with magnesium and these reagents undergo the same types of reaction as those derived from alkyl halides. In aryl halides the halogen bearing carbon is part of.
In vinylic halides the carbon that bears the halogen is doubly bonded to another carbon. Formally this is ethylene h 2c ch 2 with one of the hydrogens substituted by a heteroatom. The student asked why do vinyl halides not do the s n 2 reaction my answer was that two reasons exist for why the vinyl halide will not react with a nucleophile. An example is the addition of hydrogen chloride to vinyl chloride to yield 1 1.
Other articles where vinylic halide is discussed. From the perspective of applications the dominant member of this class of compounds is vinyl chloride which is produced on the scale of millions of.